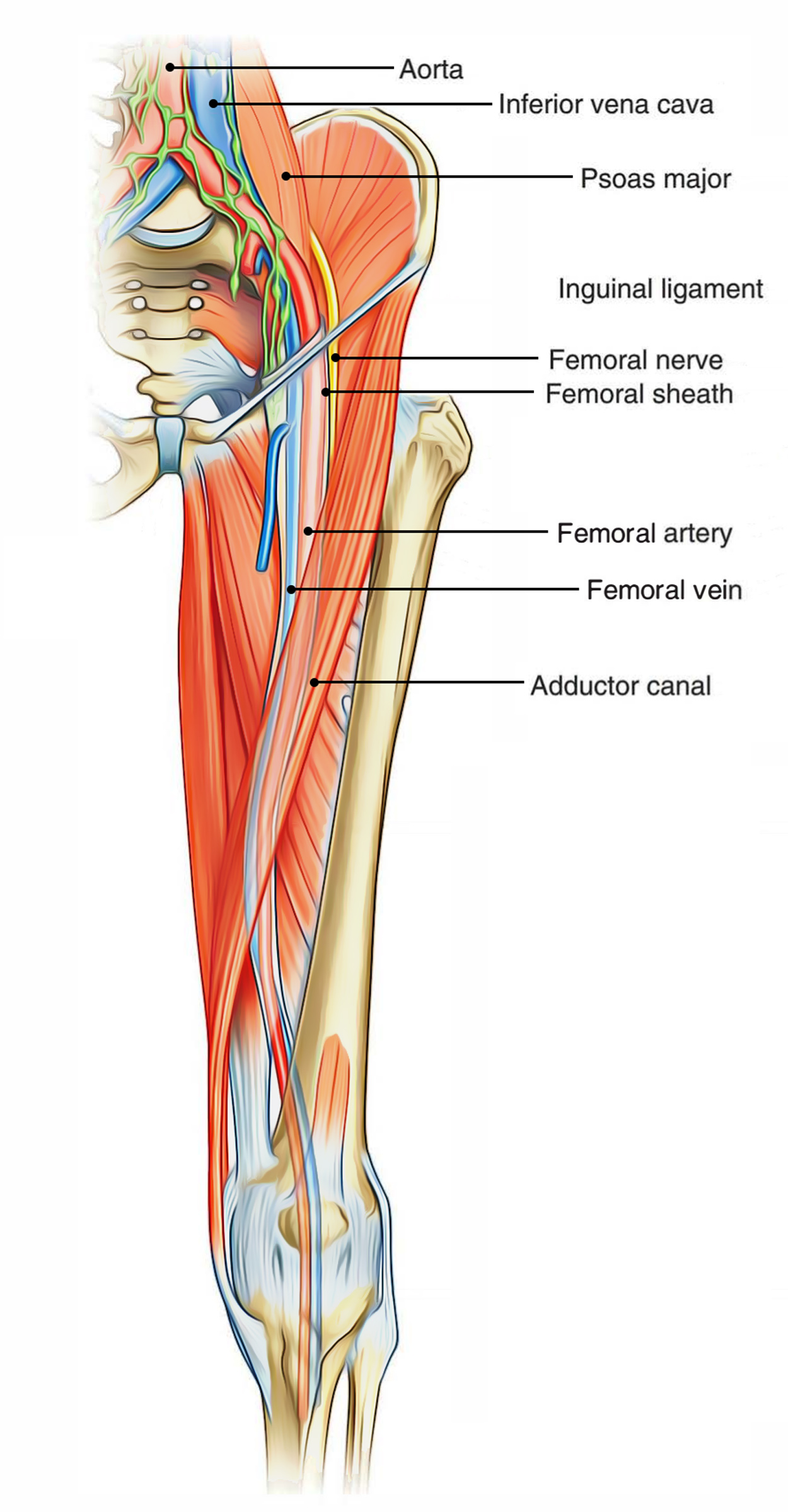
The pulsatile femoral artery lies anterior to the vein in the canal, and the saphenous nerve is seen as a round or oval hyperechoic structure anterior to the N = femoral nerve A = femoral artery V = femoral vein EL = empty space (femoral canal) and lymphatics The femoral nerve provides motor innervation to theArteries veins and nerve of the lower limb Femoral artery, Femoral vein, FemoralIt should be noted the mnemonic only pertains to the major structures and that the femoral triangle also contains the femoral sheath, femoral canal and the great saphenous vein NAVEL From lateral to medial N femoral nerve;Its contents are shown below (from lateral to medial) Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve occupies the lateral compartment of the femoral sheath along with femoral Femoral artery and its branches It emerges from the base of the femoral triangle at the midinguinal point (midpoint

Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
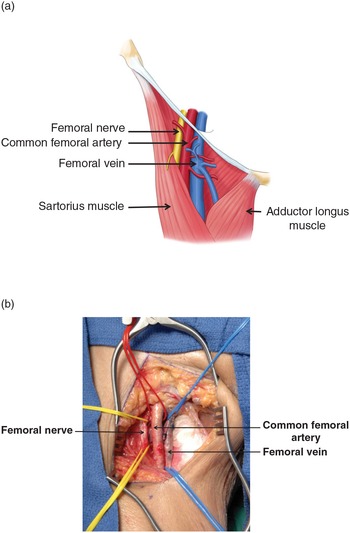
Anatomy femoral nerve artery and vein
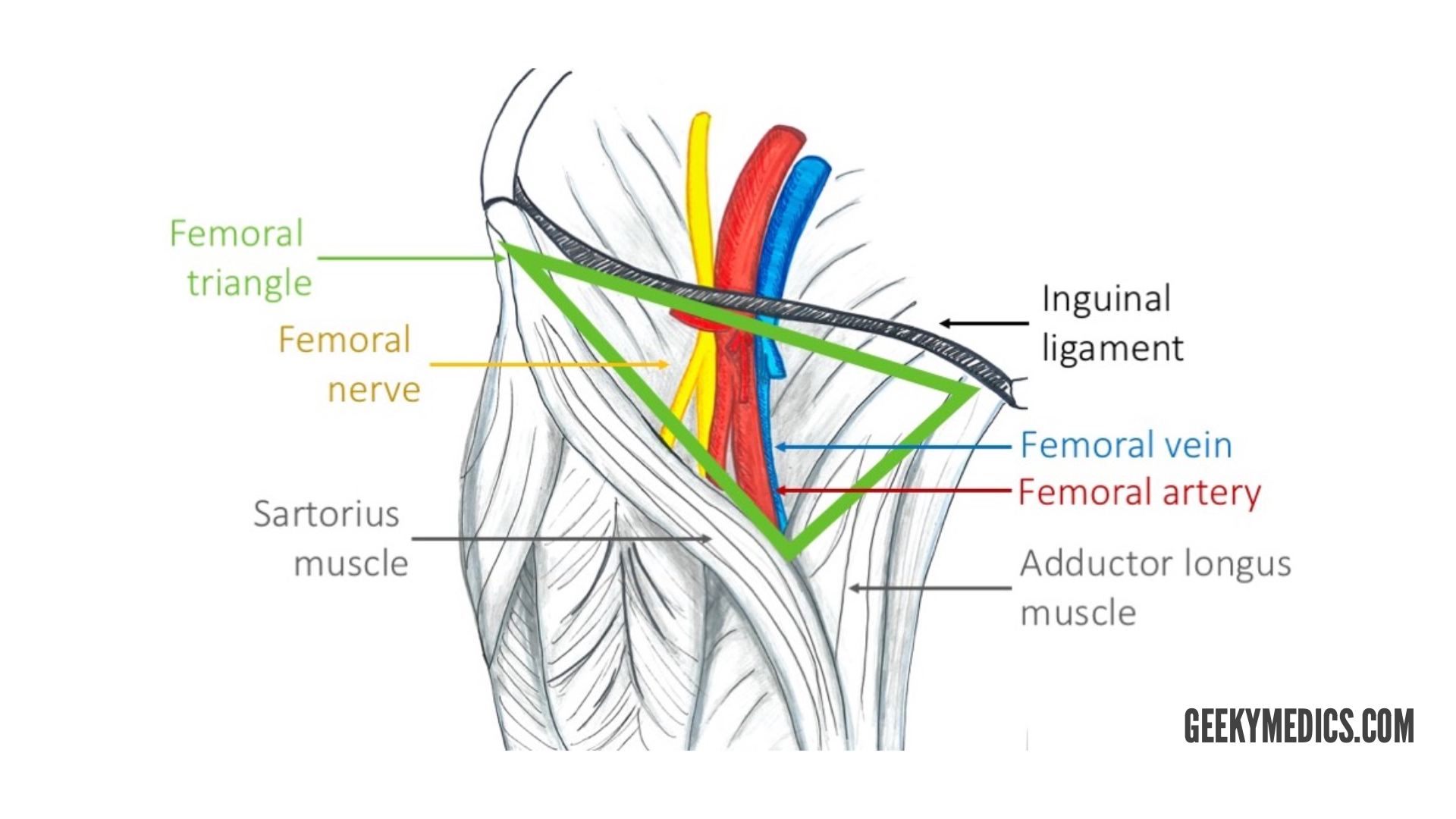
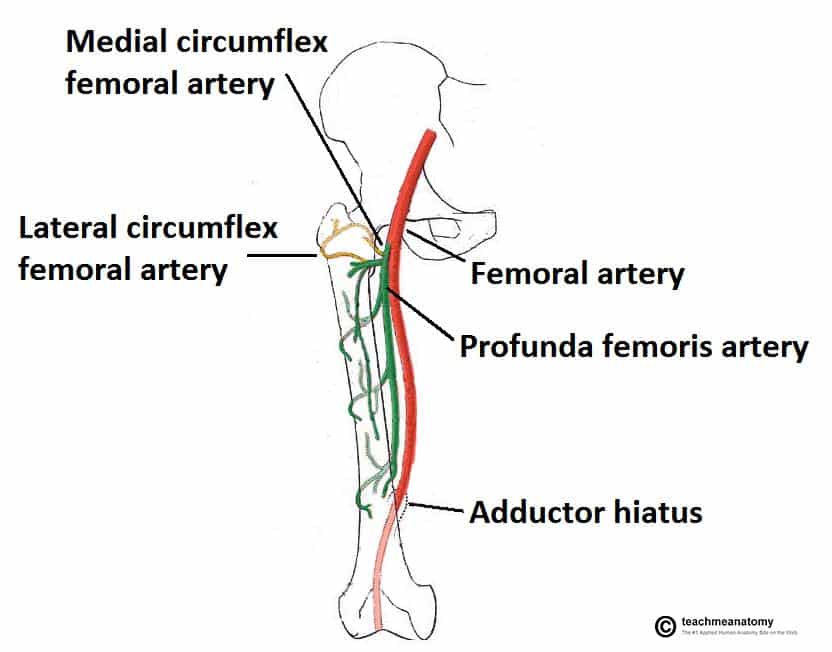
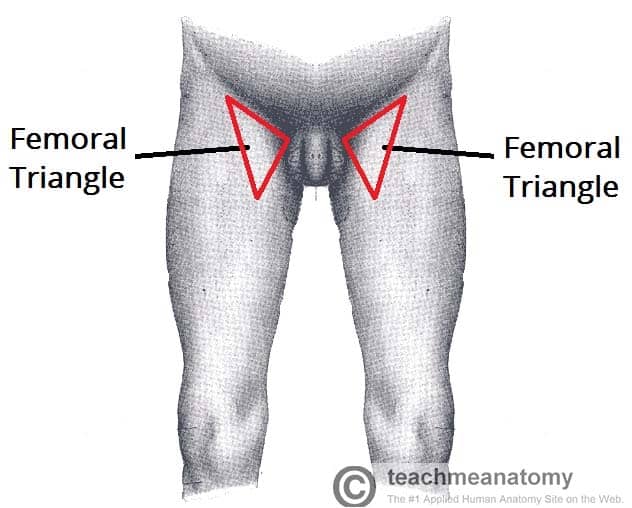
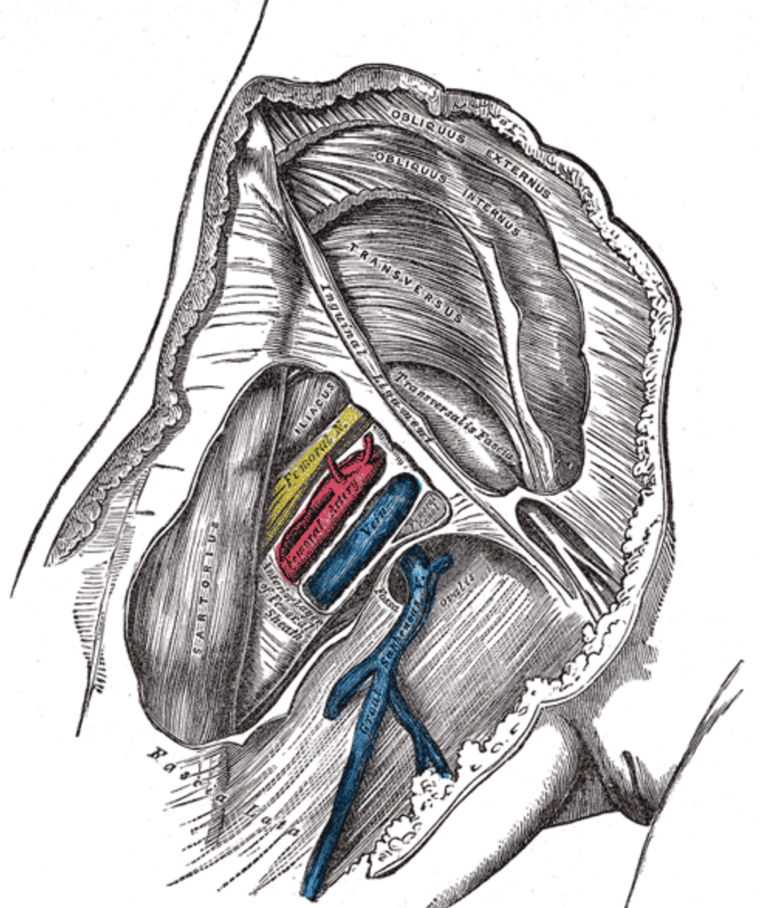
Anatomy femoral nerve artery and vein-The femoral triangle is a triangular intermuscular space in the anterior thigh through which pass major neurovascular structures (femoral artery, femoral vein, femoral nerve) Additional noteworthy anatomic regions in the thigh include the femoral canal , femoral The femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve is also lateral to the upper part of the femoral artery, within the femoral sheath, but lower down it passes to the front of the artery • 6 The profunda femoris artery a branch of the femoral artery itself, and its companion vein, lie behind the upper part of the femoral artery, where it lies on the pectineus – Lower down,Anatomy_of_femoral



Femoral Triangle Borders Contents And Mnemonics Kenhub
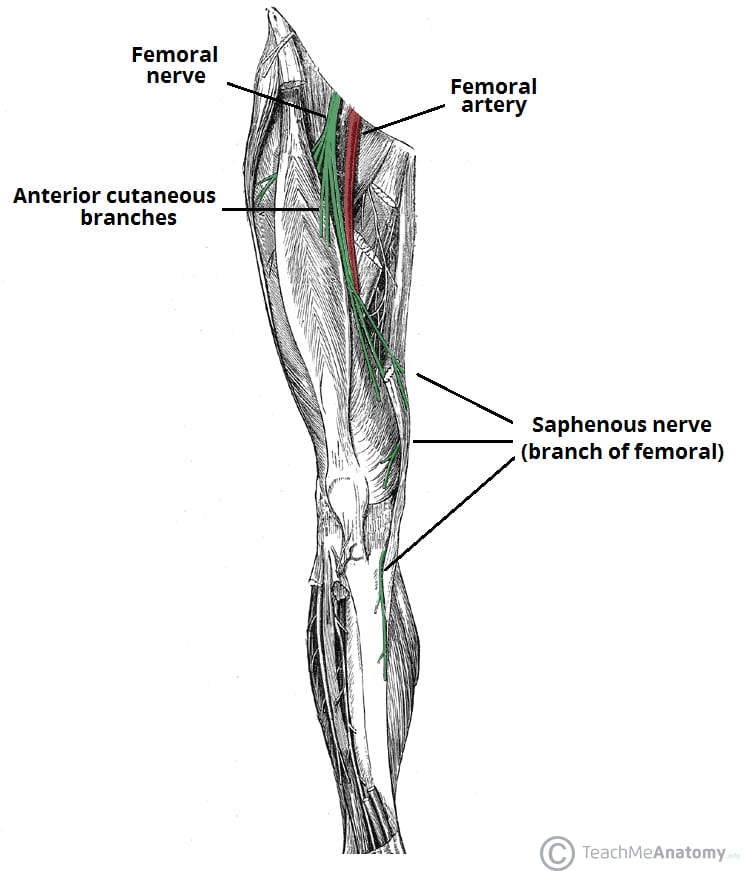
The femoral artery is a large vessel that provides oxygenated blood to lower extremity structures and in part to the anterior abdominal wall The common femoral artery arises as a continuation of the external iliac artery after it passes under the inguinal ligament The femoral artery, vein, and nerve all exist in the anterior region of the thigh known as the femoral triangle,Results In all 11 cadavers, the retractor tip was medial to the femoral nerve The mean distance from retractor tip to femoral artery and vein was 59 mm (SD = 55, range 0) and 126 mm (SD 07, range 035), respectivelyThe saphenous nerve (also long saphenous nerve, internal saphenous nerve, latin nervus saphenus) is a large cutaneous branch of the femoral nerveThe saphenous nerve contains only sensory fibers The saphenous nerve runs posterior to the sartorius, enters the adductor canal and pierces the anterior wall of the channelAfter emerging from the adductor canal, the saphenous nerve
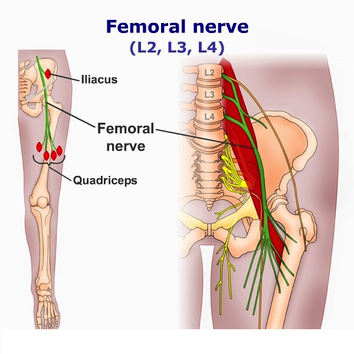
Femoral artery – Anatomy MCQ All are true regarding femoral artery except?The femoral triangle, where the femoral artery and vein are subcutaneous, represents a site where the pulse is easily taken, where arterial blood can be sampled, and where the arterial tree can be cannulated for experimental or special diagnostic procedures After arising from the lumbar plexus, the femoral nerve travels inferiorly through the psoas major muscle of the posterior abdominal wall It supplies branches to the iliacus and pectineus muscles prior to entering the thigh The femoral nerve then passes underneath the inguinal ligament to enter the femoral triangle Within this triangle, the nerve is located lateral to the femoral vessels (unlike the nerve, the femoral artery and vein
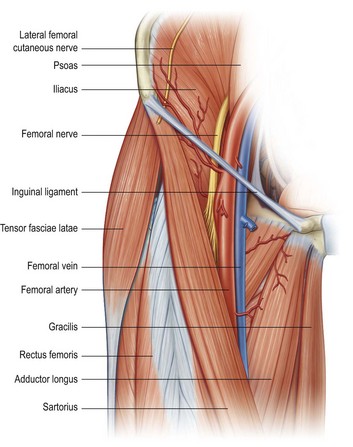
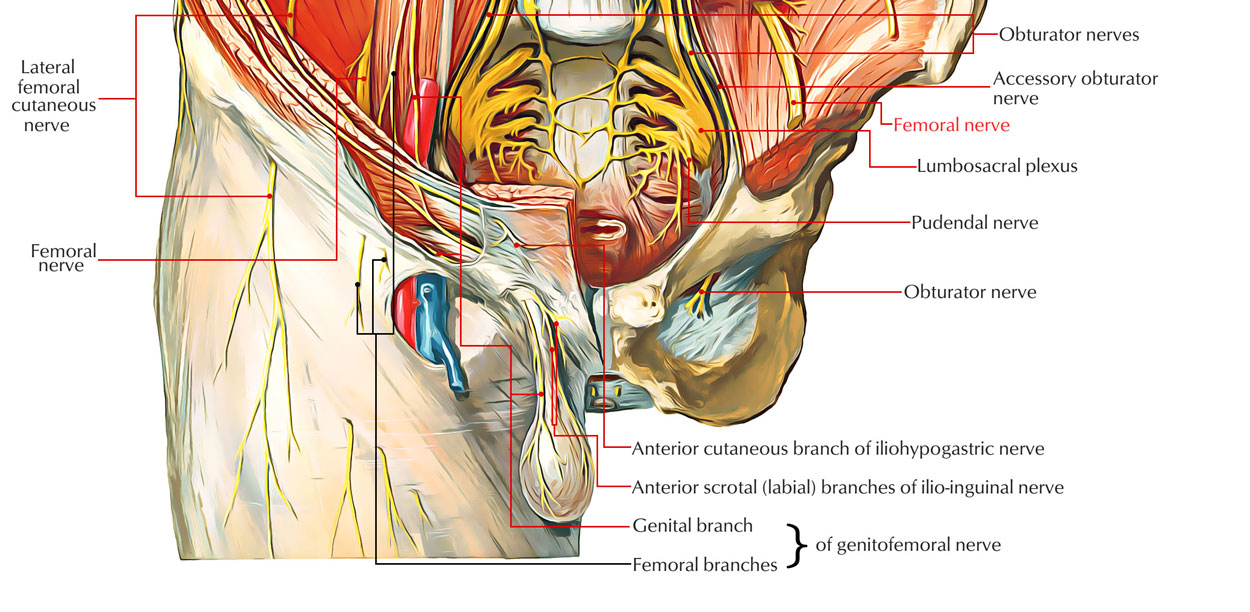
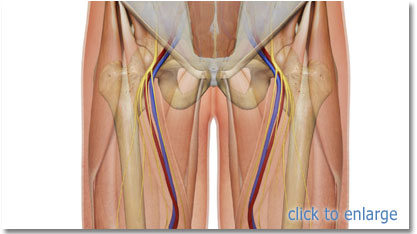
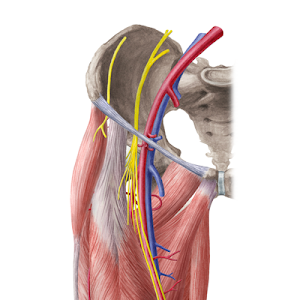
Femoral nerve – innervates the anterior compartment of the thigh, and provides sensory branches for the leg and foot Femoral artery – responsible for the majority of the arterial supply to the lower limb Femoral vein – the great saphenous vein drains into the femoral vein within the triangle The vein is posterior to the femoral artery in the apex and medial to it at the base of the Femoral Triangle It gets the great saphenous vein and profunda femoris vein and veins corresponding to the superficial branches of femoral artery Femoral Nerve The femoral nerve is located lateral to the femoral artery, outside the femoral sheath, in FEMORAL NERVE • The femoral nerve is located lateral to the femoral artery, outside the femoral sheath, in the groove between the iliacus and the psoas major • About 25 cm below the inguinal ligament it divides into anterior and posterior sections which enclose lateral circumflex femoral artery between them




Femoral Vein On Both Sides Of A Subject Right Cfv Is Formed By The Download Scientific Diagram




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
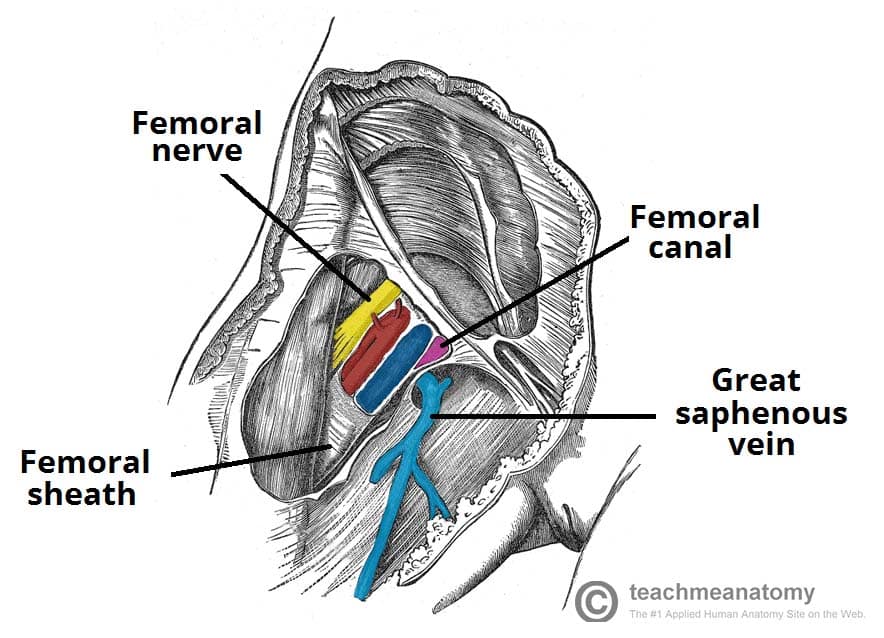
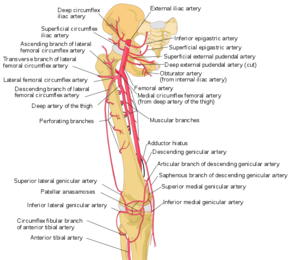
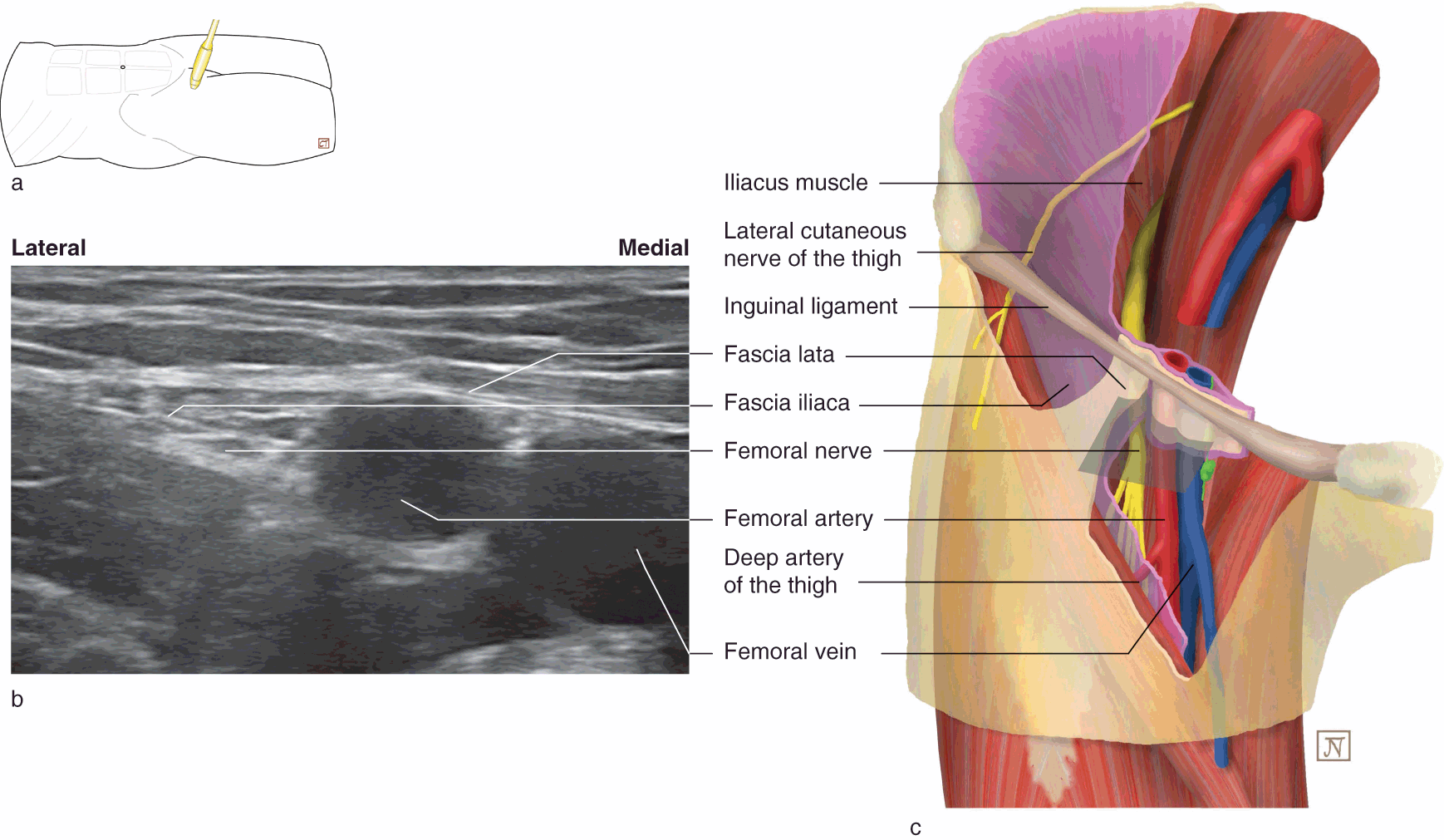
The femoral sheath encloses the femoral artery and vein, and the nerve lies outside the sheath The femoral canal is a space within the femoral sheath and medial to the femoral veinA Leaves the femoral triangle by passing through the adductor canal B Femoral nerve is lateral to the upper part of the femoral artery in the femoral triangle C Femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve is lateral to the upper part of femoral artery within the The roof is composed of skin, superficial fascia, and deep fascia The important contents, from lateral to medial, are the femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein, and the deep inguinal lymph nodes The femoral artery gives off the superficial epigastric artery, superficial and deep pudendal arteries, and the deep artery of the thigh



Limb Blocks Anesthesia Key




Untitled Document
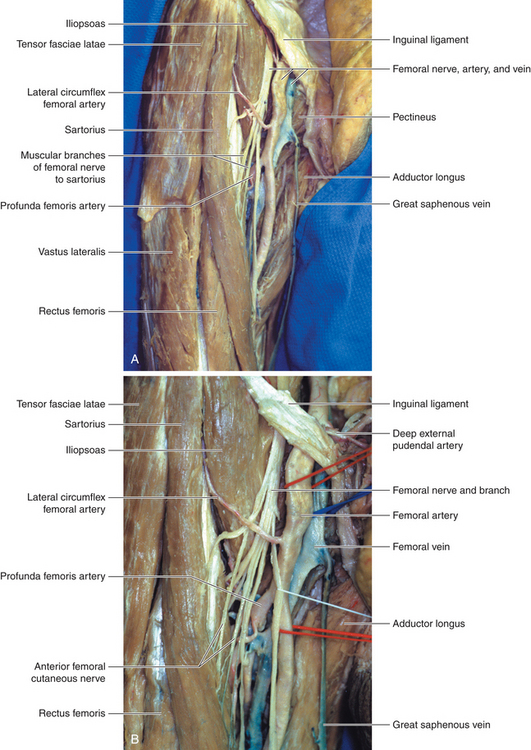
Anatomy_of_femoral_artery_and_vein 2/9 Anatomy Of Femoral Artery And Vein Therapy for Peripheral Artery Disease provides a comprehensive angiographicThe nerve descends between and provides innervation to the psoas and iliacus muscle as it courses below the inguinal ligament to enter the thigh The nerve also FEMORAL NERVE • The femoral nerve is located lateral to the femoral arteryThe femoral artery is a large vessel that provides oxygenated blood to lower extremity structures and in part to the anterior abdominal wall The common femoral artery arises as a continuation of the external iliac artery after it passes under the inguinal ligament The femoral artery, vein, and nerve all exist in the anterior region of the thigh known as the femoral triangle, just inferior toStructure The femoral artery enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery Here, it lies midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis Its first three or four centimetres are enclosed, with the femoral vein, in the femoral sheathIn 65% of the cases, common femoral artery lies anterior to the femoral vein




Anterior Thigh




Femoral Vein Anatomy Aliem
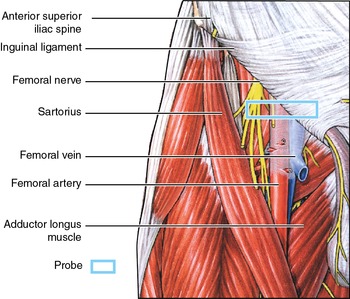
Within the triangle, identify the femoral nerve, artery and vein, and note their relationships to one another from lateral to medial Observe the termination of the greater saphenous vein Observe the femoral sheath and its compartments Identify the femoral canalThe femoral artery and vein are accessible within the femoral triangle, which is defined by the inguinal ligament superiorly, the adductor longus muscle medially, and the sartorius muscle laterally The inguinal ligament is defined as a line drawn between the symphysis pubis and the anterior superior iliac spineThe femoral vein is commonly used for intravenous infusions in infants and in patients with peripheral circulatory failure profunda femoris vein it is formed in lower part of thigh by union of perforating veins It runs close to the front of profunda femoris artery




Femoral Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora



Http Www Aivl Org Au Wp Content Uploads 18 05 Femoral Injecting Resource Pdf
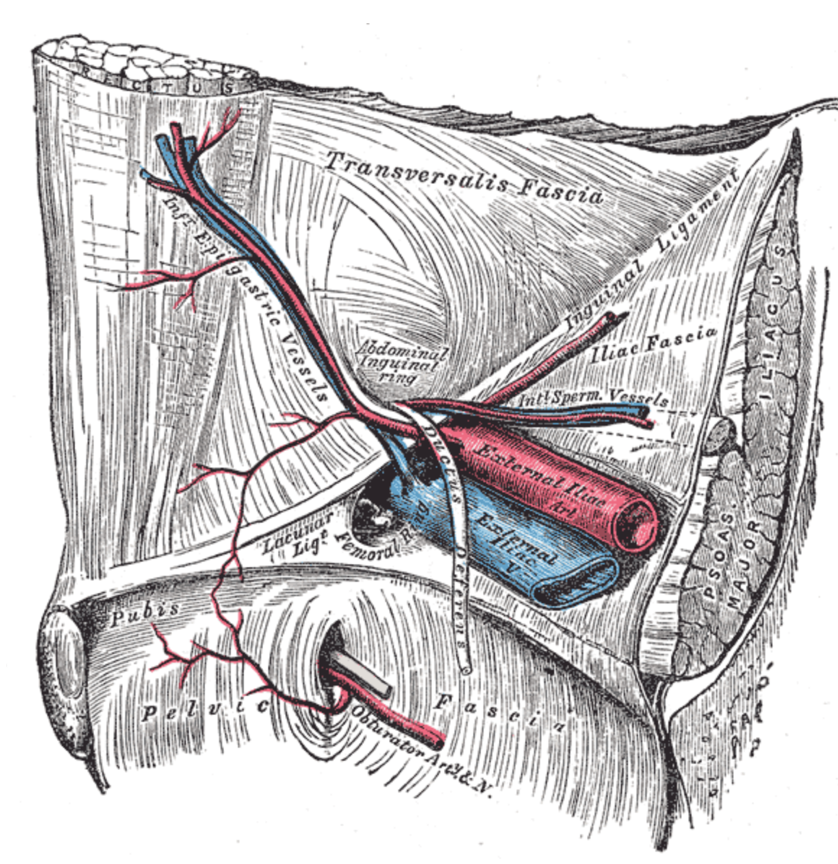
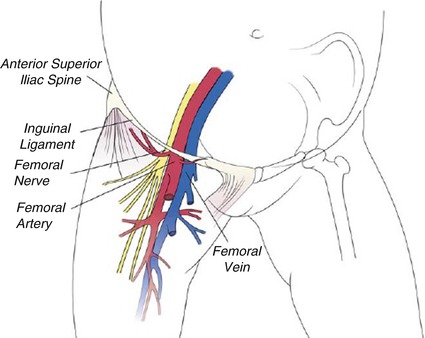
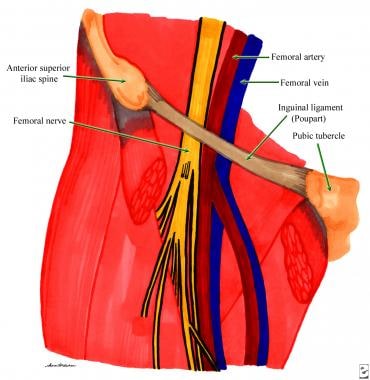
The femoral pulse is palpable at this midinguinal point NAVEL is a mnemonic for remembering the neurovascular structures that travel deep to the inguinal ligament into the femoral triangle N = femoral nerve A = femoral artery V = femoral vein EL = empty space (femoral canal) and lymphatics The deep femoral artery arises in the femoral triangle This artery crosses the femoral nerve and femoral vein in such a way as to form a delta shape near the groin region This portion is known as the femoral triangle or Scarpa's triangle3) Nerve to pectineus (note deep to fascia iliaca) Femoral sheath (inferior projection of transversalis fascia anteriorly and iliac fascia posteriorly) 1) Lateral compartment common femoral artery and genitofemoral nerve 2) Intermediate compartment femoral vein 3) Medial compartment = femoral canal lymph node and lymphatics Landmarks




Femoral Nerve Neupsy Key



The Anatomy Of Femoral Vascular Access Taming The Sru
Femoral nerve damage The femoral triangle is formed by the lateral border of adductor longus, the medial border of sartorius and the inguinal ligament (with pectineus and illiopsoas forming the floor) It contains, from lateral to medial, the femoral nerve, artery and veinArteries and Nerves of Thigh Anterior Views Anatomy Anterior superior iliac spine, Inguinal ligament, Iliopsoas muscle, Superficial circumflex iliac vessels, Superficial epigastric vessels, Superficial dissections, Tensor fasciae latae muscle (retracted), Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (cut), Sartorius muscle (cut), Gluteus minimus and medius muscles, Iliopsoas muscle, Femoral nerve, arteryThe femoral nerve lies outside the femoral sheath A way of remembering the contents of the femoral triangle is the mnemonic NAVY – nerve, artery, vein yfronts (as in briefs or pants, whatever, underwear for men) Nerve, artery, vein from lateral to medial And you've also got this branch of the femoral artery, the profunda femoris If I
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13979/Femoral_nerve.png)



Femoral Nerve Anatomy And Clinical Notes Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11126/nerves-vessels-pelvis-thigh_english.jpg)



Lower Extremities Arteries And Nerves Anatomy Branches Kenhub
Branches from the femoral nerve to mm tensor fasciae latae and adductor longus have been reported A branch was also found passing behind the femoral artery and vein, joining an accessory obturator nerve, and supplying a part of the obturator muscle The portion of the nerve arising from L4 may run a separate courseThe femoral nerve travels posterior to the inguinal ligament within the muscular lacuna The muscular lacuna also contains the iliopsoas muscle NAVEL is a mnemonic for remembering the neurovascular structures that travel deep to the inguinal ligament into the femoral triangle N = femoral nerve A = femoral artery V = femoral vein Within the femoral triangle, the femoral artery is located deep to the Skin Superficial fascia Superficial inguinal lymph nodes Fascia lata Superficial circumflex iliac vein Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve



1




Femoral Triangle Dr Bindhu S Objectives At The
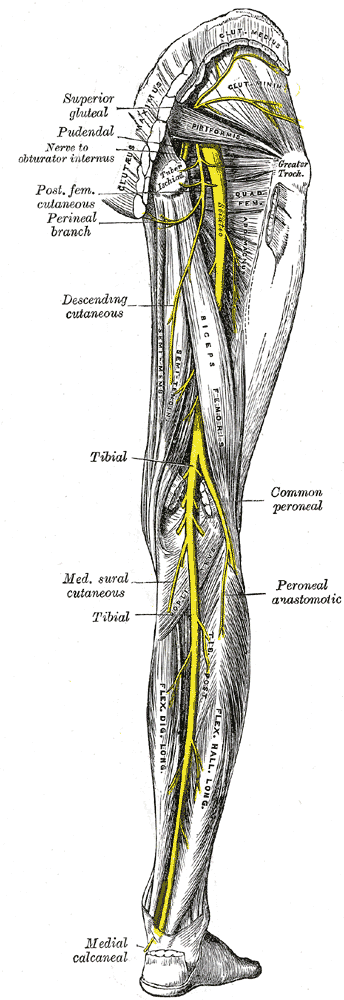
The femoral vein may remain on the medial side of the artery throughout its course in the thigh, or it may be doubled, especially in the adductor canal There is often a plexiform arrangement around the artery in this situation Femoral Vein Anatomy continuation of the popliteal vein lies in the intermediate compartment of the femoral sheath accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral triangle at the inguinal ligament it becomes the external iliac veinModel At first, the femoral nerve lies in the groove between the psoas major and iliacus, further, it leaves the pelvic cavity via the muscular lacuna Then the femoral nerve descends along the medial border of the thigh and further continues as the saphenous nerve



Easy Notes On Femoral Triangle Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab




Femoral Nerve Lateral Femoral Circumflex Artery And Vein Medial Femoral Circumflex Artery Great Saphenous Vein Profunda Femoris Artery Deep Femoral Vein Descending Branch Superficial Femoral Artery Saphenous Nerve Perforating Arteries Popliteal Vein
Nerve (femoral nerve and femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve) Artery (femoral artery) Vein (femoral vein and it's tributary – great saphenous vein) Empty space (femoral canal) Lymph node of Cloquet/Rosenmuller and Lymphatics (within femoral canal) All are contents of the femoral sheath except the femoral nerveAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators The anterior femoral cutaneous vein drains into the femoral vein From lateral to medial placement the femoral Nerve, Artery, Vein, and Lymphatics Last medically reviewed on



Easy Notes On Femoral Nerve Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab



Arterial Supply Of The Thigh And Gluteal Region Geeky Medics
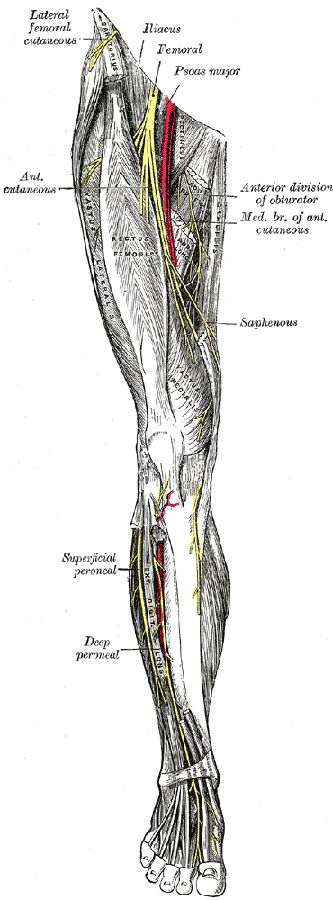
The femoral nerve is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus The nerve descends from the lumbar plexus in the abdomen, travelling down through the fibres of psoas major The nerve exits psoas major at the lower part of its lateral border, passing behind the iliac fossa to approximately the midpoint of the inguinal ligamentFemoral nerve and its branches Femoral sheath containing the femoral artery, femoral vein, and deep inguinal lymph nodes and related lymph vessels The femoral vein The femoral vein is the main blood vessel that carries oxygendeficient blood from the lower limb and back to the heart**femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve would be a more complete answer 21 The only component of the lumbar plexus that travels inferior to the




Neurovascular Structures Femoral Head Alpf Medical Research




The Femoral Triangle And Superficial Veins Of The Leg Anaesthesia Intensive Care Medicine
The saphenous nerve, artery, and vein are integral structures of a neurovascular bundle that courses through the thigh and leg of the lower limb Firstly, the saphenous nerve is a strictly sensory nerve with no motor function 1 It is responsible for innervation to the anteromedial aspect of the leg Femoral nerve (FN) as seen distally (A) and at the femoral crease (B) Note that FN is better visualized at B, before the take off the deep artery of the thigh (DAT) Femoral vein (FV) is medial to the artery FIGURE 2 (A) Crosssectional anatomy of the femoral nerve (FN) at the level of the femoral crease The FN is seen on the surface of the The proximal femoral artery and vein are wrapped in a fibrous covering called the femoral sheath This sheath is made up of several components ()The lateral part of the sheath adjacent to the femoral nerve is the continuation of the iliac fascia covering the iliopsoas muscle



Dissector Answers Anterior Medial Thigh



The Usual Vascular Access Springerlink
The femoral artery ( FA) is the continuation of the external iliac artery (EIA) at the level of the inguinal ligament As well as supplying oxygenated blood to the lower limb, it gives off smaller branches to the anterior abdominal wall and superficial pelvis On this pageE empty space (femoralDepth and dimensions of the vessels and nerves were recorded The patients' body mass indices and the depth of the femoral nerve were evaluated for correlation Results In 52% of the cases, the profunda femoral artery coursed lateral to the femoral artery, while in the others, it remained deep to the femoral artery The profunda femoral artery emerged from the femoral artery above the femoral crease in 12% of the cases, and below it in the remainder, while the lateral circumflex femoral




3 Key Areas Of The Lower Limb Simplemed Learning Medicine Simplified



Dissector Answers Anterior Medial Thigh




Femoral Artery Physiopedia




Femoral Vein Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



The Femoral Triangle Borders Contents Teachmeanatomy




The Femoral Triangle And Exposure Of The Femoral Artery Surgery Oxford International Edition




Femoral Artery Anatomy




Illustration Of The Femoral Nerve Block Region Showing The Femoral Download Scientific Diagram




Femoral Artery Femoral Nerve Arteries Mnemonics



Safe Zones For Pin Placement




Femoral Triangle




Ultrasound Guided Saphenous Adductor Canal Nerve Block Nysora




The Femoral Triangle And Exposure Of The Femoral Artery Surgery Oxford International Edition




Regional Anatomy Of A Rabbit S Thigh The Femoral Artery And Vein Download Scientific Diagram




Anatomy Lectures Femoral Artery Femoral Vein Femoral Nerve Youtube



Figure 2 A Schematic Demonstrating A Coronal View Of Normal Inguinal Anatomy Schematic Showing The Relationship Of The Artery Vein And Nerve Femoral Nerve Paralysis Following Open Inguinal Hernia Repair



Section 5 Ultrasound Theory And Point Of Care Application




Precautions For Manual Therapy Of The Lumbar Spine And Pelvis



Hip And Thigh Arteries Veins And Nerves Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube




Femoral Artery Wikipedia




Femoral Triangle Wikipedia




Anterior Medial Thigh Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet




Lower Extremity Peripheral Nerve Blocks Femoral Nerve Block




Femoral Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora



Femoral Artery Physiopedia



Arteries Of The Lower Limb Thigh Leg Foot Teachmeanatomy
/GettyImages-87302280-83604c7a3ca84315a84304a002377404.jpg)



Femoral Vein Anatomy Function And Significance




Psoas Major Muscle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Thigh Knee And Popliteal Fossa Knowledge Amboss



The Femoral Triangle Borders Contents Teachmeanatomy



Femoral Nerve Neurologyneeds Com




Femoral Nerve Neupsy Key




Femoral Artery Wikipedia



The Anatomy Of Femoral Vascular Access Taming The Sru



Precautions For Manual Therapy Of The Lumbar Spine And Pelvis




Lower Limb Anatomy The Femoral Triangle Ponder Med




Healthy Street Anatomy Of Femoral Triangle The Femoral Triangle A Subfascial Formation Is A Triangular Landmark Useful In Dissection And In Understanding Relationships In The Groin In Living People It Appears



Femoral Nerve Neupsy Key



1



Femoral Triangle Borders Contents And Mnemonics Kenhub



How Is Femoral Nerve Block Administered For Pain Management



Femoral Artery Injuries Chapter 35 Atlas Of Surgical Techniques In Trauma




Medical Addicts Info The Femoral Triangle Of Scarpa The Femoral Triangle Of Scarpa Is An Anatomical Region Of The Upper Inner Human Thigh Boundaries It Is Bounded By Superiorly The Inguinal




Femoral Triangle Sketchy Medicine




Close Proximity Of The Femoral Nerve Femoral Artery And Femoral Vein To The Acetabular Retractor Trialexhibits Inc



Femoral Vein Sonoanatomy For Anaesthetists




S F Physical Exam Flashcards Quizlet



The Lower Limb Chapter 8 Applied Anatomy For Anaesthesia And Intensive Care



The Femoral Nerve Course Motor Sensory Teachmeanatomy




Femoral Sheath And Inguinal Canal Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants Gross Anatomy Medical Anatomy Medical School Studying
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/vena-femoralis-2/7kNnjd2McgZ18lAMpcxsA_V._femoralis_01.png)



Femoral Triangle Borders Contents And Mnemonics Kenhub



Femoral Region And Hernias Anatomy Lecturio Medical




Total Hip Replacement Doctor Stock



Http Yxylxs Yzu Edu Cn Jpx Content Upload File 0502 Pdf




Special Anatomical Regions Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed



Femoral Nerve Block




Anatomy Bony Pelvis And Lower Limb Saphenous Nerve Artery And Vein Article




Anatomy Of The Femoral Nerve Artery And Vein Medical Illustration




Thigh Knee And Popliteal Fossa Knowledge Amboss




Lower Limb Anatomy The Femoral Triangle Ponder Med
/CloseupoflegwhileexercisingPeterDazeleyGettyImages-bf452734667d45ae8756ef7286e24cfd.jpg)



Femoral Artery Anatomy Function And Significance



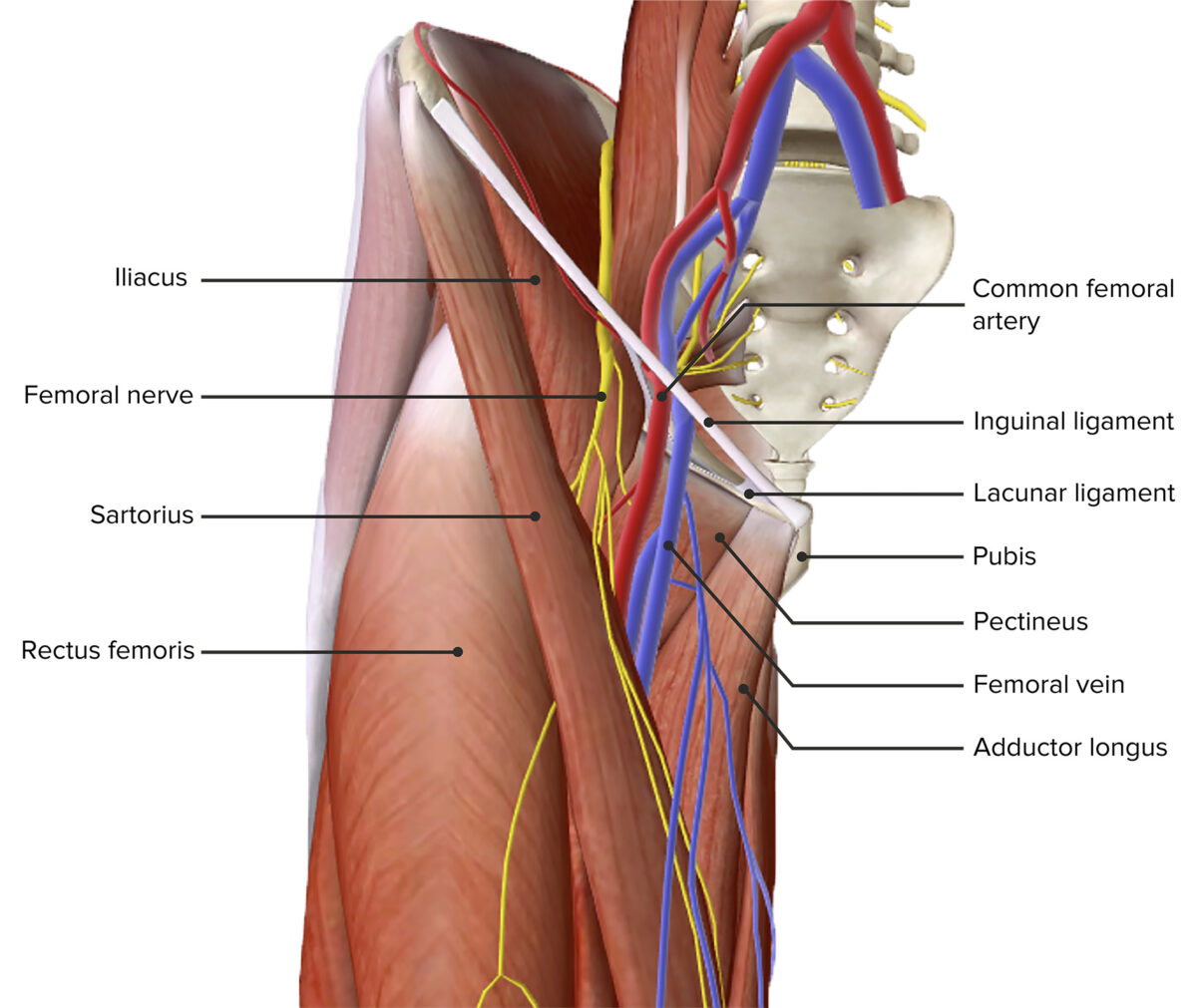
Common Femoral Artery Basicmedical Key
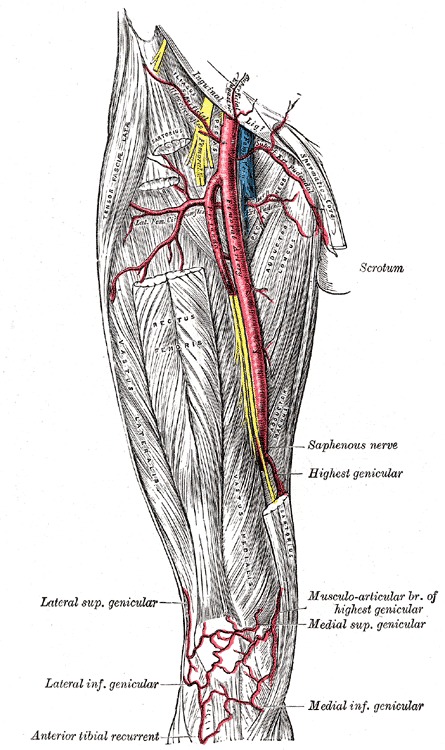



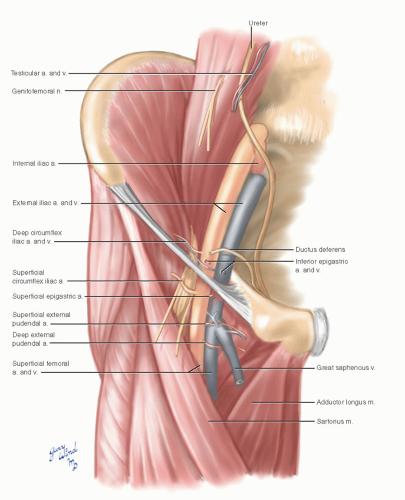
Figure Femoral Artery And It S Branches Contributed By Gray S Anatomy Plates Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
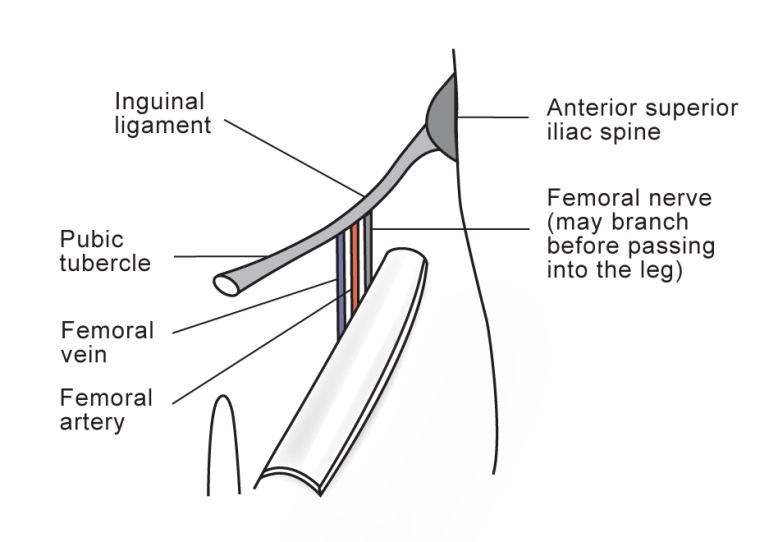



Femoral Nerve Block



1




Ultrasound Guided Adductor Canal Block Anesthesia Key



Femoral Region Gastrointestinal Medbullets Step 1




Femoral Artery Prohealthsys
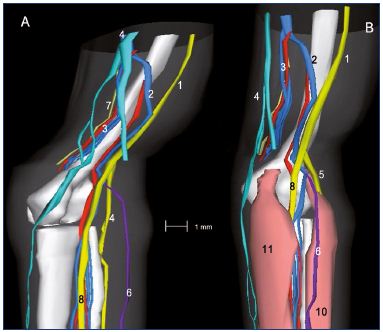



Focus On Venous Embryogenesis Of The Human Lower Limbs Servier Phlebolymphologyservier Phlebolymphology
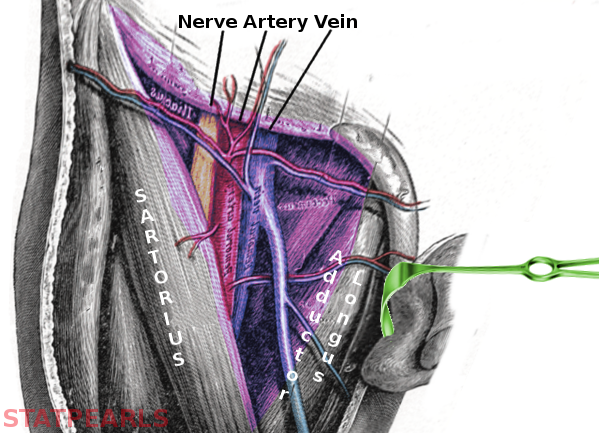



Anatomy Abdomen And Pelvis Femoral Triangle Article
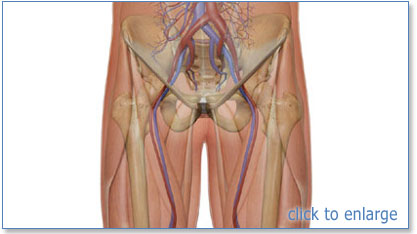



Section 2 Anatomy And Physiology



Cambridge Orthopaedics Uk



An Unusual Case Femoral Artery Compression



1
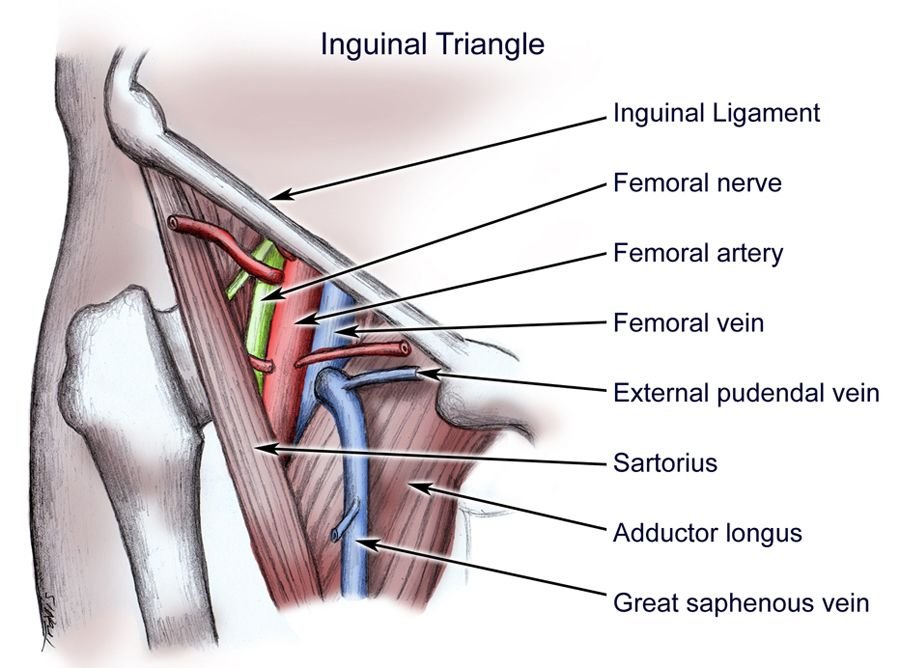



Femoral Triangle Borders Contents And Clinical Importance Medical Junction




Safe And Smart Dry Needling Round Three




Externally Rotate Leg For Femoral Vein Access Femoral Nerve Arteries Anatomy



Http Ksumsc Com Download Center Archive 1st 439 2 muscloskeletal block Team work Anatomy 18 vascular anatomy of the lower limb Pdf
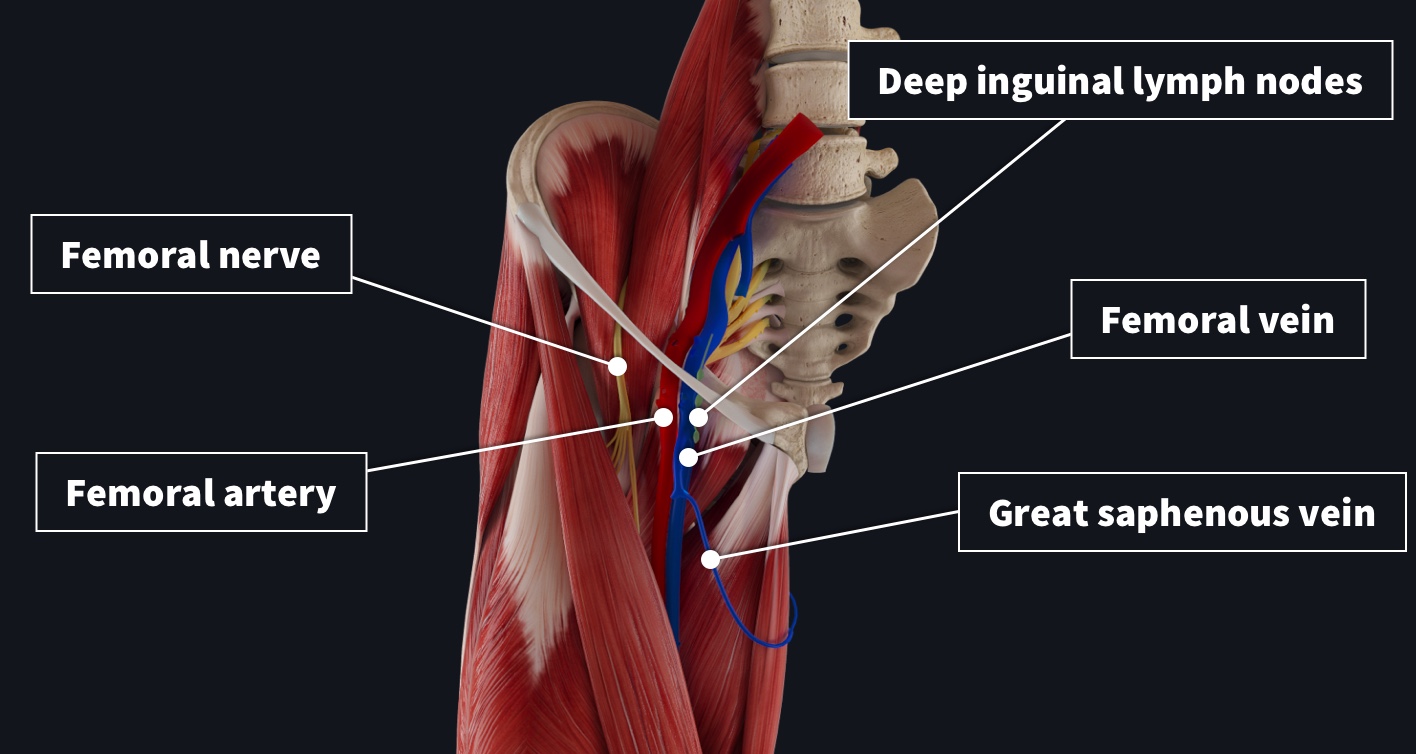



Remember The Contents Of The Femoral Triangle With This Crafty Mnemonic Complete Anatomy



Http Ksumsc Com Download Center Archive 1st 435 2 muscloskeletal block 435 teamwork Anatomy Vascular anatomyof the lower limb Pdf
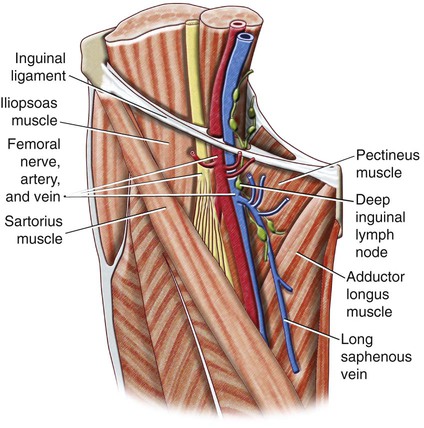



Anatomy Of The Lower Limb Radiology Key




ɹǝʇlnoԁ Piʌɐᗡ 𝔹𝕖 𝕜𝕚𝕟𝕕 Pa Twitter Anatomy Of The Femoral Triangle 1 Femoral Artery 2 Femoral Nerve 3 Femoral Vein 4 Anterior Superior Iliac Spine 5 Inguinal Ligament 6



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿